TL;DR
|
Hotel budgeting and forecasting drive profitability for every hotel in the hospitality industry. Every hotel manager needs hotel budgeting and forecasting to make precise budgets and allocate resources efficiently.
However, hotels saw room revenue and total operating revenue fall below budget in 2025. Plus, they faced unpredictable OTA fees and softer demand across regions. In fact, rooms revenue fell 12%, while ADR landed 4% below budget expectations. Meanwhile, U.S. hotels saw RevPAR nearly 9% below budget in early 2025 data. Only the gross operating profit margin remained strong, falling just 1.2% below budget. This shortfall highlights the need for accurate forecasting, forecasting tools, and data-driven insights.
Hotels that adopt data-driven insights and advanced forecasting software improve financial performance and avoid costly missteps. This article will explain hotel budgeting and forecasting fundamentals and show how these tools foster strategic decision-making and financial health.
What is Hotel Budgeting?
A hotel budget is a financial plan that outlines projected income and expenditures for a specific period. It supports hotel budgeting and revenue management across the property. Hotel managers use it to monitor financial performance and make strategic decisions. The budget relies on historical data and market trends to create more accurate forecasts.
Some of the key components of a hotel budget include:
- Rooms revenue: Projected income from room bookings.
- Food & beverage (F&B): Revenue from restaurants, bars, room service, and banquets.
- Operations: Day-to-day costs including utilities, supplies, and maintenance.
- Marketing: Advertising, promotions, digital campaigns, and OTA commissions.
- CAPEX: Planned capital expenditures like renovations or equipment upgrades.
- Fixed and variable expenses: Payroll budget (staff salaries, benefits, and incentives) and utilities.
This financial plan helps streamline financial planning, track key metrics, and improve financial outcomes. Effective hotel management uses the budget to allocate resources efficiently across the hospitality industry.
To manage finances more effectively, hotels often separate annual budgets from departmental budgets. Here’s how:
| Budget Type | Purpose | Scope | Key Focus |
| Annual Budget | Provides a comprehensive hotel-wide financial plan | Total hotel revenue, operating costs, and capital expenses | Tracks key metrics, ensures long-term financial stability, and guides strategy |
| Departmental Budget | Breaks the annual plan into smaller, actionable units | Specific departments such as Rooms, F&B, Spa, Marketing | Focuses on hotel operations, fixed and variable expenses, and revenue streams |
What is Hotel Forecasting?
Hotel forecasting differs from budgeting in its focus and flexibility.
For example, forecasting uses real financial data, performance metrics, and market trends to predict what will happen next. It updates estimates frequently to improve accuracy in forecasting and adjust strategy. In contrast, budgeting sets financial goals and a comprehensive hotel budget for a future period. It sets fixed targets during the budget creation process and stays relatively stable.
Hotels rely on two main types of forecasts:
- Rolling forecasts: Continuously updated forecasts that adjust for the latest occupancy trends, market conditions, and competitor activity.
- Monthly forecasts: Short-term predictions focusing on the next 30 days or a month, providing operational teams with actionable data.
Accurate forecasting gives hotel managers insights to optimize revenue, adjust variable expenses, and manage operating costs smartly. In fact, hotels with precise forecasts improve strategic decision-making and protect financial health against uncertainty.
Key Data Required for Hotel Budgeting & Forecasting
Hotel managers create precise budgets and forecasts by combining multiple critical data sources. Below is a breakdown of the key financial indicators that guide hotel budgeting and forecasting:
- Historical financial data: Past income and expense patterns reveal trends and guide financial outcomes. Managers analyze these records to improve the hotel budgeting process accuracy.
- Occupancy forecasts: Projected room bookings help managers plan revenue and allocate resources efficiently. These forecasts directly affect room revenue and operational decisions.
- ADR trends: Tracking average daily rates informs pricing strategies and supports overall financial goals. This helps predict future performance more accurately.
- Market demand indicators: Local and regional trends reveal shifts in traveler behavior. Hotels use this data for strategic decision-making and forecasting.
- Revenue segmentation: Breaking revenue down by department or service shows which areas drive profit. Managers track performance metrics to optimize profitability.
- Expense patterns: Analysis of variable expenses and operational costs helps improve financial health. Understanding patterns reduces waste and enhances budgeting accuracy.
- Labor cost benchmarks: Staffing trends and payroll data guide efficient resource allocation. This aligns with the budget creation process and cost management.
- Event calendar: Local events influence demand and revenue opportunities. Hotels integrate this data into forecasts to maximize profitability.
- Competitor intelligence: Monitoring competitors’ pricing strategies helps hotels adjust rates. This ensures accurate forecasting and better market positioning.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a Hotel Budget
Building a hotel budget might seem complicated, but a clear, structured approach simplifies the process. A good budget ensures long-term financial stability, supports strategic planning, and guides financial planning throughout the year.
By following these steps, hotel managers can create precise budgets and confidently allocate resources efficiently across all departments.
1. Define revenue goals
Start by establishing clear revenue goals for your hotel. Consider all revenue streams, including room rates, food and beverage, spa services, and event income.
For example, instead of setting a vague target like “increase revenue,” define it as “achieve $450,000 room revenue in Q2.” Specific goals allow your team to plan operational and marketing activities effectively. Clear revenue targets also guide resource allocation, ensuring that departments with the highest potential receive sufficient support.
Your goals will guide the rest of the budget forecasting process. Keep these goals visible so everyone understands your hotel’s financial direction. Revisit them throughout the budgeting cycle to stay aligned with market shifts.
2. Use occupancy & ADR forecasts
Once revenue goals are defined, use occupancy and ADR forecasts to project room revenue. Occupancy shows how many rooms are expected to sell, while ADR indicates average income per room.
For instance, if occupancy is forecasted at 75% and ADR is $150, you can estimate $112,500 in room revenue for a month. Adjust for seasonality, local events, and historical trends to improve accuracy. Accurate forecasting reduces surprises and supports budget forecasting across the hotel.
By combining these projections with other financial data, you can anticipate peak demand and plan staffing or promotional strategies efficiently.
3. Build departmental budgets
Break your hotel budget into departmental sections:
- Rooms
- Food & beverage
- Spa services
- Events and banquets
- Marketing
Each department needs a plan for revenue and operating expenses. For example, housekeeping requires cleaning supplies and payroll. Food & beverage budgets include ingredients, labor, and promotions.
Departmental clarity helps allocate resources efficiently and track financial reporting accurately. You can also collaborate with department heads to ensure realistic forecasts. Well-prepared departmental budgets support effective hotel budgeting and operational efficiency.
4. Estimate variable & fixed costs
Identify all expected variable costs and fixed costs. Variable costs change with occupancy, including guest amenities, housekeeping supplies, and hourly labor. Fixed costs remain constant, such as property taxes, insurance, and long-term contracts.
Also consider planned capital expenditures such as renovations, technology upgrades, or equipment replacement. Don’t forget unexpected expenses, such as emergency repairs, that could disrupt your financial plan. Using historical data for variable and fixed costs helps improve financial projections and overall operational efficiency.
5. Model GOP & NOI
Once revenue and costs are defined, calculate Gross Operating Profit (GOP) and Net Operating Income (NOI) to understand hotel profitability. These metrics guide resource allocation and support long-term financial stability.
The GOP shows a profit after subtracting operating costs from total revenue. Use this formula:
GOP = Total Revenue − Operating Costs
For example, if:
- Total revenue: $1,000,000
- Operating costs (labor, utilities, amenities, departmental expenses): $700,000
GOP = 1,000,000 − 700,000 = 300,000
This means your hotel retains $300,000 after covering all operational costs. Modeling GOP lets managers test scenarios, such as:
- Occupancy drops by 10%
- Room rates increase by 5%
- Seasonal fluctuations affect revenue streams
By adjusting these variables, you can estimate how changes impact profitability before they happen.
Similarly, NOI accounts for fixed costs like property taxes, insurance, and debt service. To calculate NPI, use this formula:
NOI = GOP – Fixed Costs
For example, if:
- GOP: $300,000
- Fixed costs (taxes, insurance, debt): $50,000
NOI = 300,000 − 50,000 = 250,000
This means the hotel earns $250,000 after paying all operating and fixed costs. Calculating NOI helps hotel managers:
- Understand actual profitability
- Test the effect of capital expenditures
- Plan for unexpected expenses
By modeling GOP and NOI, you create a dynamic tool to forecast financial outcomes, monitor key metrics, and ensure the budget supports your hotel’s strategic objectives.
6. Validate assumptions
Before finalizing, review every assumption in your budget. Compare revenue targets with market room rates, cost estimates with supplier agreements, and occupancy forecasts with recent trends.
Ask questions like:
- Are my occupancy forecasts realistic for upcoming events?
- Do my departmental cost estimates reflect current vendor rates?
- Could competitor promotions impact revenue expectations?
This step makes sure your budget reflects real-world conditions, minimizes errors, and maintains credibility with leadership.
7. Present final budget
Finally, present the budget to leadership in a clear, digestible format. Use charts, tables, and visuals to show revenue, operating expenses, GOP, and NOI. Explain how assumptions, forecasts, and departmental budgets support overall financial planning and strategic planning. Highlight areas that may require careful monitoring, such as unexpected expenses, high operating costs, or capital expenditures.
For example:
- Rooms: $500,000 revenue, $150,000 operating costs
- Food & Beverage: $200,000 revenue, $80,000 variable costs
A well-presented budget helps management understand financial priorities and makes it easier to approve resources. It also guides continuous monitoring throughout the year, enabling adjustments as market conditions or financial projections change.
How to Build a Hotel Forecast (Step-by-Step)
Accurate hotel forecasting helps managers make informed decisions and optimize profit margins. Here’s how you can do that:
1. Start with occupancy forecasting
Begin by projecting how many rooms your hotel will sell over a period. Use historical data, seasonality, and current booking trends to identify patterns.
For example, analyze the last three years of occupancy during the same season. Adjust for upcoming local events or holidays that might influence demand.
Accurate occupancy forecasting forms the backbone of making hotel budgeting decisions. It also helps prevent human error by basing predictions on measurable trends rather than intuition.
2. Forecast ADR based on demand
Once occupancy is estimated, project your Average Daily Rate (ADR). Align pricing strategies with predicted demand to maximize room revenue. High-demand periods may allow you to increase ADR, while low periods require adjustments.
Monitor competitor rates and historical ADR trends to set competitive pricing.
3. Estimate RevPAR and total room revenue
Combine occupancy and ADR to calculate Revenue per Available Room (RevPAR). Use this formula:
RevPAR = Occupancy % * ADR
For instance, if occupancy is 80% and ADR is $150, RevPAR = $120.
Then multiply RevPAR by the total number of available rooms to estimate total room revenue.
This step links your forecast to actual financial performance, helping you create budgets and predict future performance.
4. Forecast other revenue streams
Rooms aren’t the only source of revenue. Include:
- Food & Beverage (F&B) sales
- Spa and wellness services
- Event or banquet income
- Ancillary services like room service or parking
Estimate each stream based on past trends, bookings, and market demand. Incorporating multiple revenue sources creates a comprehensive budgeting approach that supports numerous departmental budgets.
5. Update cost forecasts
Adjust operating costs and variable expenses according to expected occupancy and other revenue streams. To do so,
- Consider labor, utilities, and consumables for higher occupancy periods
- Include fixed costs like property taxes, insurance, and planned capital expenditures
This step ensures your hotel forecasting is aligned with profit margins and operational efficiency, helping hotel managers make proactive resource allocation decisions.
6. Compare forecast vs budget
After preparing forecasts, compare them with your budget to identify discrepancies. For example, if forecasted F&B revenue is 10% below budget, investigate staffing or promotional strategies. Then, review both room revenue and ancillary revenue streams for variance analysis.
This step highlights areas where adjustments may be necessary, improving budget creation and optimizing revenue. Continuous comparison prevents surprises and guides strategic decision-making.
7. Re-forecast weekly or monthly
Forecasting is not static. You have to update it regularly using forecasting tools to reflect real-time bookings, cancellations, or market shifts.
- Weekly re-forecasts help adjust staffing or promotions proactively
- Monthly reviews allow course correction for long-term financial performance and profit margins
Regular re-forecasting reduces human error and ensures your projections remain accurate for future performance. Combining updated forecasts with hotel forecasting systems strengthens hotel budgeting decisions and maximizes revenue potential across the lodging industry.
Budgeting & Forecasting Formulas + Examples
A strong hotel budget relies on clear formulas to accurately predict financial outcomes. Using standard calculations helps managers track profit margins, control operating costs, and improve forecast accuracy.
Here are the most important formulas every hotel manager should know.
1. Revenue formulas
Revenue forecasts are the foundation of making hotel budgeting decisions. The primary formulas are:
Total Room Revenue = Occupancy × ADR × Available Rooms
For example, if:
- Occupancy: 80%
- ADR: $150
- Available Rooms: 100
Total Room Revenue = 0.8 × 150 × 100 = 12,000
Total hotel revenue also includes F&B, spa, and other revenue streams.
2. Cost-per-occupied-room (CPOR)
CPOR measures the variable costs associated with each occupied room. To calculate it:
CPOR = Total Variable Costs/Number of Occupied Rooms
For example, if:
- Total Variable Costs: $4,000
- Occupied Rooms: 100
CPOR = $4,000/100 = 40
This allows managers to monitor operating expenses, plan staffing, and control day-to-day operational costs.
3. GOPPAR calculations
It measures profitability for each available room, helping track profit margins and forecast financial performance.
GOPPAR = Gross Operating Profit/Available Rooms
For example, if:
- GOP: $50,000
- Available Rooms: 200
GOPPAR = $50,000/200 = 250
Use GOPPAR to compare performance across different periods or properties. It helps hotel managers identify inefficiencies and optimize revenue streams.
4. Forecast accuracy formulas
Accurate forecasts reduce human error and improve strategic planning. Use these formulas to measure prediction accuracy:
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): (1/n) * Σ(|Actual – Forecast| / |Actual|) * 100%
For example, if:
- Actual Room Revenue: $12,000
- Forecasted Revenue: $11,500
MAPE = |12,000−11,500|/12,000 × 100 = 4.17%
Lower MAPE values indicate more reliable hotel forecasting, enabling effective budgeting and better financial projections.
To track forecast accuracy over time:
- Calculate monthly or weekly accuracy
- Adjust assumptions for future forecasts
- Identify patterns in booking, market demand, or seasonality
Common Challenges Hotels Face
Hotels face real challenges when building budgets and forecasts, and these issues can hinder performance. Let’s take a look at them:
1. Inaccurate data
Many hotels struggle with inaccurate or fragmented information, which affects budgeting and forecasting and leads to poor decisions. Systems like PMS, RMS, CRM, and rate shopping often don’t communicate well with each other. When data remains siloed, managers lack a complete view of metrics such as occupancy, ADR, and other key performance indicators.
According to a recent report, 49% of hoteliers struggle to access critical data, while 18% cite inaccurate data as a significant barrier to personalization and revenue optimization. This leads to inconsistent forecasts and reactive planning.
To avoid this, hotels should invest in integrated systems and forecasting tools that unify data daily. Data governance, daily checks, and regular audits can keep information accurate and timely. Strong data governance improves planning and prevents errors in financial planning and creating budgets.
2. Over-optimistic revenue assumptions
Hotels frequently set revenue forecasts based on past performance without accounting for dynamic market forces. This can be especially risky in volatile economic environments.
For example, Hilton cut its 2025 RevPAR growth forecast from 2–3% to flat to 2% due to economic uncertainty and softer travel demand. This highlights how over-optimistic assumptions can misalign goals with reality.
Using realistic occupancy and ADR forecasts based on current demand helps prevent budget shortfalls. Regular updates and scenario planning keep revenue targets grounded in real demand conditions.
3. Lack of segmentation
Failure to break forecasts into clear segments makes planning harder. Without proper segmentation of revenue sources, hotels miss nuanced patterns.
Segmentation reveals how different services perform under various conditions. It also helps align pricing strategies with specific traveler segments.
4. Manual spreadsheets
Despite advances in RMS and analytics, many revenue teams still rely on manual spreadsheets. In fact, teams often spend excessive hours manually stitching data, delaying insights and reducing responsiveness.
Modern budgeting platforms, including cloud-based RMS, BI tools, and API integrations, automate calculations, maintain consistent data, and free staff to focus on insights rather than number crunching.
5. Market volatility
External shocks like economic shifts, tariffs, and changing travel patterns create instability in demand and pricing. High-profile cases, such as hotels revising growth expectations due to macroeconomic volatility, show how unpredictable conditions can erode revenue forecasts.
To avoid this, revenue managers must build agility into revenue strategies by using real-time market intelligence and adaptive pricing models. Dynamic pricing tools that factor in competitor rates, local demand, and booking pace can help hotels stay responsive in turbulent markets.
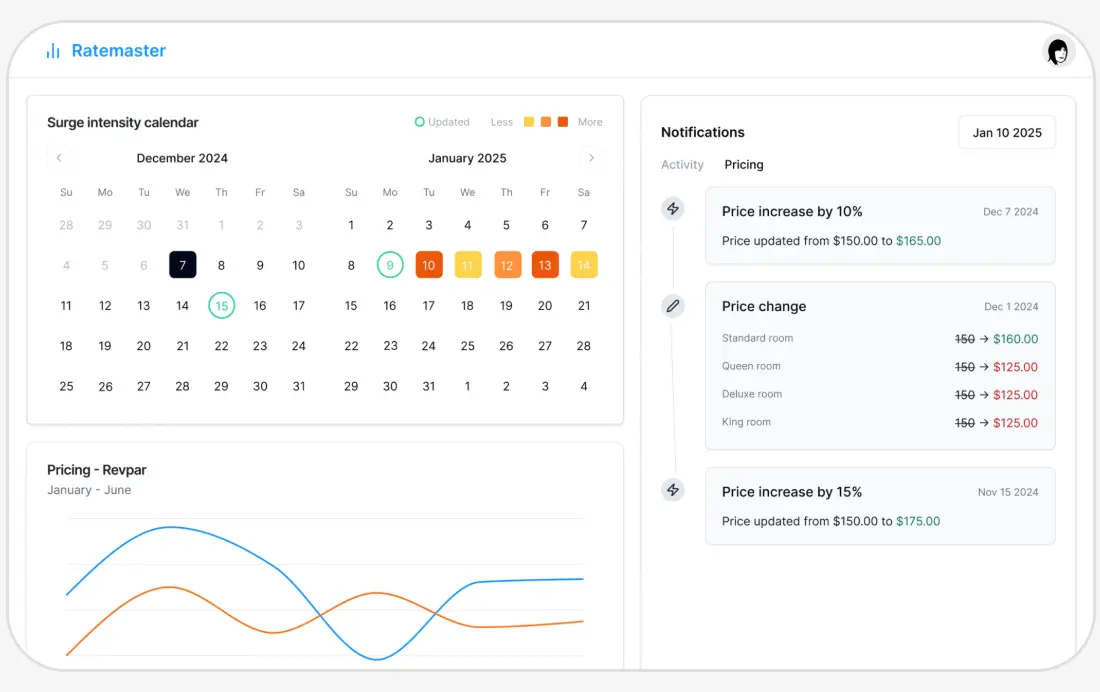
Modern Tools for Hotel Budgeting & Forecasting
Modern revenue systems connect forecasts, pricing, and budgets into one continuous workflow. This approach improves operational efficiency, supports effective budgeting, and enables sustainable growth in volatile markets.
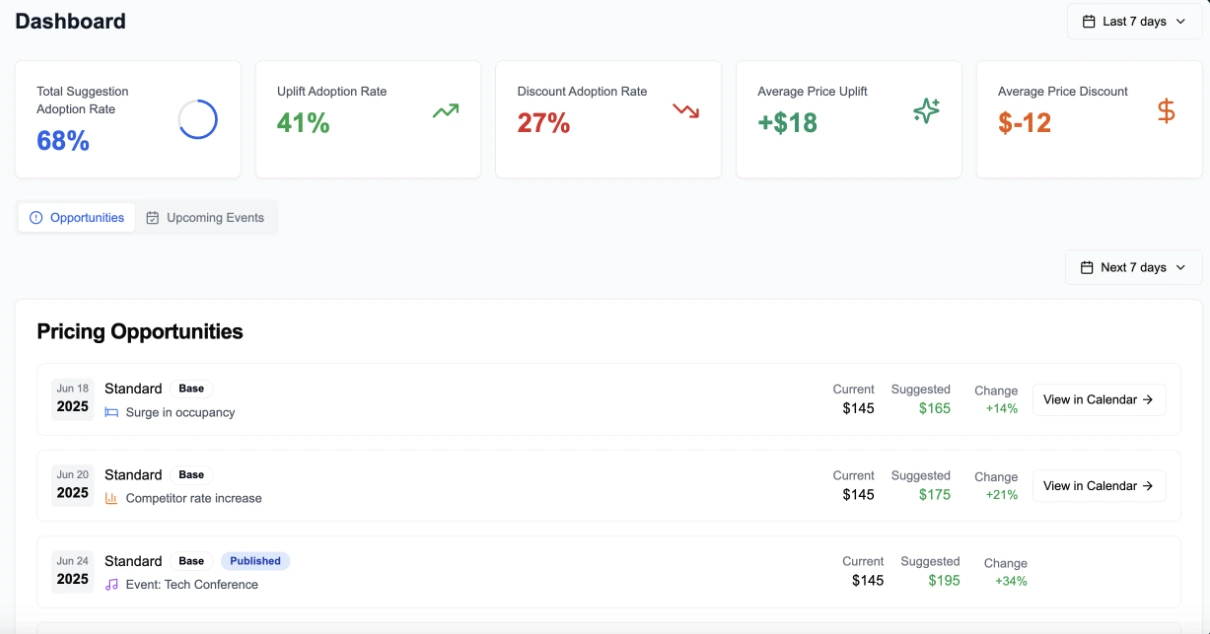
Here’s how ampliphi RMS is redefining how hotels approach pricing and profitability through AI optimization.
A. Real-time data forecasting
Every booking brings a different revenue opportunity for your hotel. Some guests book low-demand periods, while others fill high-value peak dates. ampliphi RMS continuously analyzes these booking patterns and adjusts prices in real time.
Instead of relying on static discounts, the system evaluates occupancy forecasts, booking pace, and market demand. This approach helps hotels stay competitive while protecting margins. Revenue teams no longer wait weeks to react to demand shifts. They adjust pricing as conditions change.
Recent industry research confirms the impact of this approach. In fact, hotels using AI-driven pricing achieved RevPAR gains of up to 35%. These gains came from faster reactions to demand forecasting and automated pricing decisions.
B. Automated budgeting suggestions
Managing multiple room types and distribution channels manually creates risk. Spreadsheet updates often introduce errors, delays, and missed revenue opportunities. ampliphi RMS eliminates this friction through automation.
The platform updates rates dynamically across all room categories and channels. It monitors booking behavior and adjusts pricing without manual intervention. This automation supports smarter resource allocation and more consistent financial planning.
Hotels using automated pricing workflows report several advantages:
- All OTAs and direct channels update simultaneously
- Teams react instantly to competitor and market changes
- Staff spend less time adjusting rates and spreadsheets
Over time, these automated adjustments improve confidence in pricing decisions. They also create stronger alignment between daily pricing actions and budget expectations.
C. Predictive analytics
Many traditional pricing models struggle with seasonality and lead-time effects. ampliphi RMS addresses this gap using advanced analytics that evaluate historical and forward-looking demand together.
For example, if corporate events drive demand spikes during certain weeks, the system recalibrates rates automatically. This foresight helps hotels avoid underpricing while remaining competitive. It also supports better planning for departments like room service and spa services, which depend on demand visibility.
D. Integrations with PMS
Forecasting and budgeting tools only work when systems communicate seamlessly. ampliphi RMS integrates directly with property management systems (PMS) to create a unified data environment.
These integrations eliminate manual data transfers and reconciliation work. Booking data, rates, and forecasts flow automatically between systems. This connectivity improves operational efficiency and reduces human error.
Integrated systems also provide actionable insights across departments:
- Finance teams align forecasts with budgets
- Operations teams plan staffing accurately
- Revenue teams adjust pricing with confidence
Together, these benefits support effective budgeting and long-term profitability.
Best Practices for More Accurate Budgets & Forecasts
Accurate hotel budgets and forecasts require discipline, structure, and continuous refinement. These best practices help hotels stay realistic, agile, and profitable across changing market conditions.
- Use segmented data: Aggregated data hides patterns that directly impact revenue and cost behavior. Segmenting data gives clarity and reveals where performance truly shifts.
- Validate assumptions regularly: Every budget relies on assumptions about demand, pricing, and costs. When teams fail to revisit assumptions, forecasts drift from reality. Validate assumptions monthly or even weekly during volatile periods. You can also compare actual performance against forecasts and identify gaps quickly.
- Incorporate event impact: Events create demand spikes that traditional averages often overlook. Ignoring event impact leads to underpricing and staffing shortages. Build known events directly into forecasts. Review historical performance during similar events. Then, adjust occupancy, rates, and departmental costs accordingly.
- Use dynamic pricing forecasts: Static pricing assumptions limit forecast accuracy in changing markets. Dynamic pricing forecasts respond to real-time booking pace and demand signals.
Turning Hotel Budgets & Forecasts into Competitive Advantage
Hotel budgeting and forecasting drive financial success when teams use them strategically. Budgeting defines a clear financial roadmap, while forecasting empowers hotels to respond to market changes in real time.
Modern technology, AI, and automation tools like ampliphi RMS make these processes faster, more accurate, and actionable. As a result, hotels control costs, maximize revenue, and respond proactively to demand shifts.
Book a demo to see how ampliphi RMS simplifies hotel budgeting and forecasting.
FAQs
1. What is hotel budgeting and forecasting?
Hotel budgeting sets revenue, expense, and profit targets for a defined period. Forecasting predicts future performance using real-time data to adjust operations and financial plans.
2. How do hotels prepare their budgets?
Hotels define revenue goals, forecast occupancy and ADR, allocate departmental expenses, estimate costs, model profitability, validate assumptions, and present a finalized budget.
3. What are the 7 steps of forecasting?
The seven steps of forecasting are gathering historical data, analyzing booking pace, segmenting demand, accounting for seasonality and events, evaluating market conditions, adjusting for cancellations, and applying forecasting formulas. These steps help hotels accurately predict occupancy, room revenue, and operational needs.
4. What are the 7 steps to budgeting?
The seven steps to budgeting are defining revenue goals, using occupancy and ADR forecasts, building departmental budgets, estimating variable and fixed costs, modeling GOP and NOI, validating assumptions, and presenting the final budget. This process ensures effective budgeting and aligned financial planning.
5. How often should hotels forecast?
Hotels should re-forecast monthly, weekly during peak seasons, or whenever demand shifts. Regular forecasting improves accuracy, captures market changes, and supports strategic decision-making.
6. What tools can improve hotel budgeting accuracy?
Forecasting tools, property management systems, and RMS platforms like ampliphi improve budgeting accuracy. They streamline data, reduce human error, and provide actionable insights for financial reporting.
7. What is the difference between a budget and a forecast?
A budget is a fixed financial plan for a set period. A forecast predicts future performance using real-time data. Budgets guide spending, while forecasts help hotels adjust plans to maximize profit margins and operational efficiency.